So if something goes wrong, you can restore your Internet connection

In the digital home, DSL failures are very annoying. PCs and phones cannot connect to the Internet, streaming media does not work, and even smart homes are struggling. We will first show you how to locate the error. We then show you specific troubleshooting steps and possible alternatives.
DSL failure: checklist
If you know your way out, you can quickly troubleshoot with a checklist. Otherwise, we will guide you step by step to explain. Take the time to limit your mistakes, and this will help someone who can help you later, whether it's a helpful neighbor or the support of a provider.
Step 1: Check the hardware
Check the hardware first, and sometimes simply restart the working miracle here. In the same step, you check the network settings of your smartphone or PC. You will also need this data for the next steps.
Step 2: Check the connection to the router
The next step is to test the connection to the router. Therefore, you are still in your local network environment, but the first step is to troubleshoot errors in your home network.
Step 3: Check the [basic] connection to the Internet
If the router is running and accessible, you are now checking your connection to the Internet. To rule out potential sources of error, only IP checks were performed initially.
Step 4: Check your internet connection, including DNS
The last step is to check the connection including DNS. This corresponds to the functionality of all your applications or browsers.
Possible choice
Are you working here normally, or your internet connection is working, or there is a problem with your service provider. In the latter case, we will show you other options that will still get you back online.
Check your router and cables
It's always worth a look at the router. If all the lights are on and the cable does not seem to be working, the first step is to simply unplug it. After two minutes, you can insert the plug again.
This simple method can solve many connection problems. There are many reasons why a router must be restarted, most of which are "hanging up" somewhere in the device. Turning the power on and off again resets all features in the router and then restarts. The settings are retained.
Find out the IP settings
Each device in the home network is assigned a unique IP. These are usually assigned by routers and can be identified as "standard gateways" in the network. First check the IP you have, and the IP of your router [standard gateway].
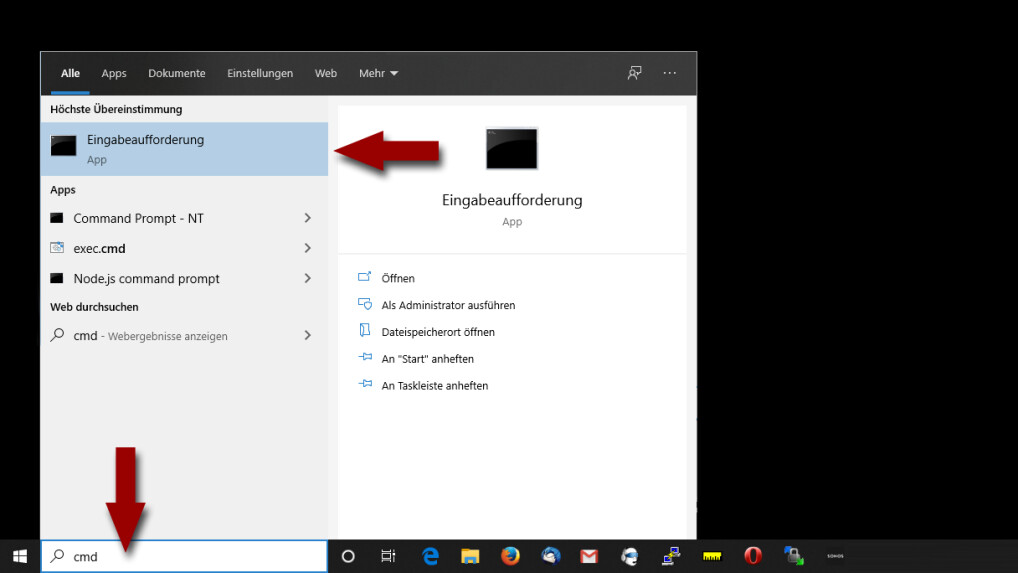
DSL Failure-Step 1: Open Command Prompt
Open the start menu and enter "cmd". You should then see "Command Prompt" in the start menu. Open it with "Enter" or click on the application entry.
Finding the default gateway
Then type "ipconfig" at the command prompt and press "Enter". This will show the IP settings, which in the simplest case will look exactly the same as the settings on the screenshot. Note that there may be several entries listed here. Usually you are looking for someone with "192.168." To boot, which is the default setting for most routers. In any case, you should find an entry with a registered "standard gateway".
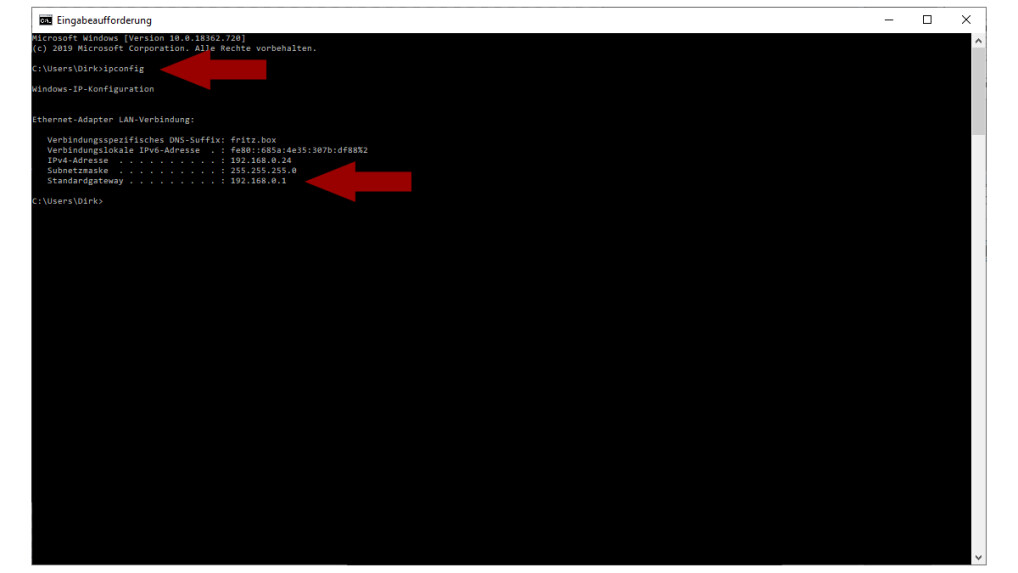
DSL Failure-Step 2: Finding IP Settings
If you find the entry, remember the IP address and then you need it in the next step. The good news so far is that your device seems to be reaching the router, which has at least one IP address assigned by the DHCP server.
Your device cannot connect to the router. This can have a variety of reasons, from a shutdown DHCP server [or an intervening DHCP server] to a hardware problem. So please check if
ping router
Enter "ping% IP%" at the prompt. In this case, replace "% IP%" with the IP address from the previous step. In our example, "ping 192.168.0.1". In our example, you can see the successful answer with the green arrow. The second error was intentionally entered, which is the result of the error.
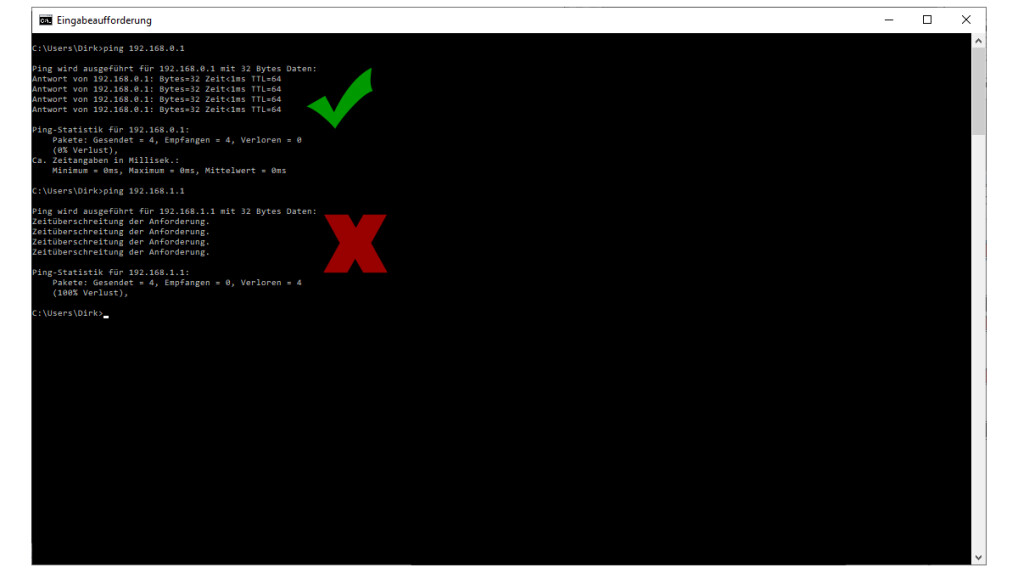
DSL Failure-Step 3: Check the connection to the router
If it works for you and you see something similar to the image above, you can access the router through the network. You have now eliminated basic local issues and can move on to the next step.
If there is no answer or the error message "Request timed out", you are not connected to the router. Therefore, your device will not even enter the router. Again, first check if
Check internet connection
The good news so far: you have no local issues. At a minimum you want to create a connection to the router and then check the connection to the Internet in the following steps. This also works best through the command prompt, where the browser provides only limited help.
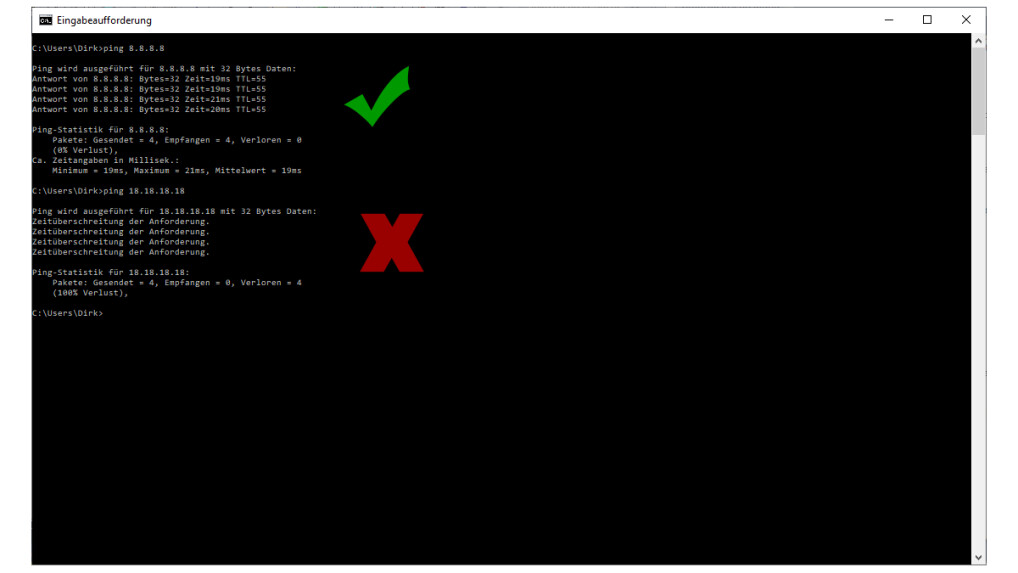
DSL Failure-Step 4: Check the connection to the Internet
The server you "ping" is actually always accessible: Google's public DNS server. To do this, enter the "ping 8.8.8.8" command at the command prompt. In our example, we used the wrong IP address "18.18.18.18" for demonstration purposes.
Do you see the results next to the green arrow? Then you can in principle be on the Internet. Don't worry if there is a "request timeout" entry. This may happen from time to time, but it is important that most answers are yes. You can recognize this from the line that starts with "8.8.8.8 … Starting to answer".
If you only see the message "Request timed out," the router cannot access the Internet. Before turning everything upside down, you should first check our fault detectors and see if your provider is faulty. The most important providers can be found directly in the list, all other providers can be found in the fault report.
Report a failure to a supplier
If your provider is down, it's worth reporting as this is the only way the provider can be active on its own. The following table provides contact details for the most important providers.
| provider | telephone number |
|---|---|
| 1 and 1 | 07 21 96 00 |
| SF | 08 00 33 01 00 0 |
| Kabel Germany | 08 00 52 66 62 5 |
| Oxygen 2 | 08 00 52 51 37 8 |
| Vodafone | 08 00 17 21 21 2 |
DSL provider hotline in case of failure
If no faults are displayed, the access data should be checked again. We will use Fritzbox as an example to illustrate the setup.
Check DNS server
If your line has successfully passed the above steps, you are now checking if DNS is working properly. On the Internet, he is responsible for not having to enter the aforementioned IP address, but for "netzwelt.de" or "google.de" in the browser. To do this, you can also use the command prompt and enter the command "ping google.de" here.
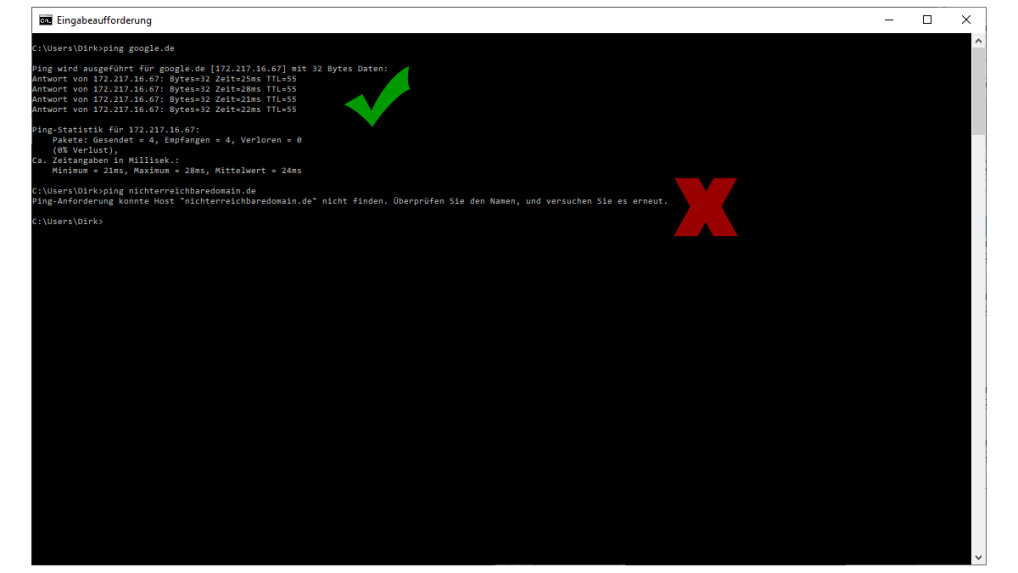
DSL Failure-Step 5: Check DNS Server
If you see a positive answer here, you have no DSL issues. If some sites still deny service, the problem may be with them, and some of them may also happen locally, for example, Netflix works in Hamburg and Google works in Munich, but Netflix does not want to do this.
You can check by entering the URL of the corresponding service and checking Netflix with "ping netflix.com". Alternatively, you can view our fault indicators and look for problematic services, and we will show you where the faults are currently in Germany. If this outage is local, using a VPN will help, as it will find other ways to reach its destination.
You are now experiencing problems, but you have localized it: DNS server. The good news is that you can sometimes fix this yourself. In this guide, we explained how to change the DNS server.
You can surf the Internet in the following ways: tethering and WiFi hotspot
If your provider is down, it will not be resolved in a few minutes. For example, if you still want to go online because you work in your home office, various options will help you.
The easiest option, especially in densely populated areas: ask neighbors if they can use their internet. It sounds silly, but sometimes you don't see the forest covered trees. It sounds simple, but the transmission power of modern routers usually works. Just remember that you are a guest on his network, and maybe you won't make any major downloads or streaming. For your own security, you should also be aware that you are on an external network and sometimes a VPN is installed here.
If your neighbors are too far apart, your phone can help you. Although this comes at the cost of data volume, quick troubleshooting can justify the additional cost. You have several solutions here, you can
All variants have their pros and cons, but they can still get you back on the internet soon. However, these are only permanent solutions in special cases, but they are always suitable as an alternative or backup.
Article keywords
Network, DSL hardware and technology, and routers
Image Source
FreeImages.com/mike gieson
Table of Contents