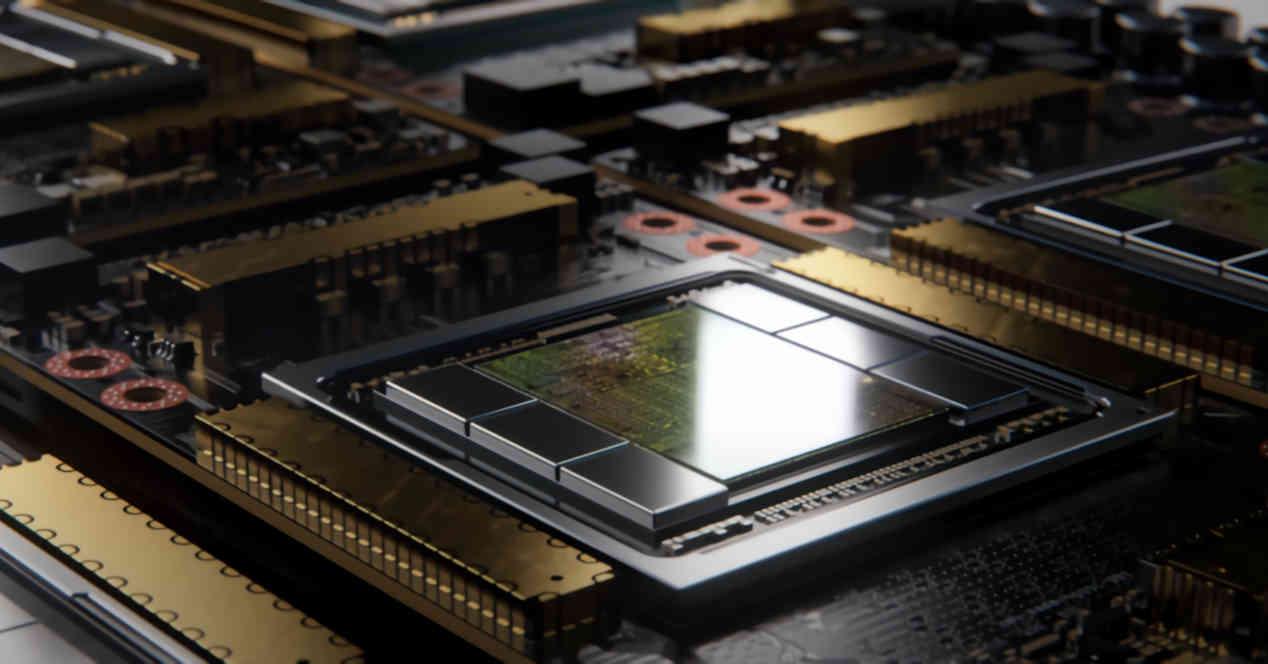
Graphics cards are one of the main parts of a PC, without them we couldn’t use them because it couldn’t communicate with us through the monitor screen. But, in recent years, the size of the graphics chip has increased dramatically.
GPUs are getting bigger and bigger
One of the observations that can be made by looking at the size of the different processors that have appeared in recent years is that if we are talking about pure processors or SoCs, we will see that the size has remained stable, whereas in the case of GPUs, it increases more and more over time.
This phenomenon has been happening in GPUs for a long time and has a reason for being which has to do with the way all GPUs work and their main task, which is to make the graphics faster and faster than the previous one and with a level higher. .Retail.
Two different philosophies: TLP vs ILP
TLP stands for Thread Level Parallelism or Thread Level Parallelism, while ILP stands for Instruction Level Parallelism. These are the two main philosophies when designing a processor that will run code in parallel.
In CPUs, we try to improve their ILP, which is why at each generation the number of instructions per execution thread that each core can execute is improved. When we talk about single-threaded or single-threaded performance, we are talking about how a kernel works by running part of the program on its own. This is due to the fact that the programs executed by the CPUs are for the most part sequential and therefore in series, with possible elements of parallelism. This is why in a CPU, increasing the number of cores several times does not increase the performance of a program in a linear fashion.
On the other hand, GPUs work differently, they don’t run programs but rather run them are what we call “waves” which are made up of threads of execution, but whereas in a CPU a thread can be a single thread. long sequence of instructions, in a single thread GPU this can be something as simple as a single instruction with your data. This is why in GPUs we try to increase their performance by adding new cores and therefore their size increases more and more.
GPUs will continue to grow in size
One of the current issues is the fact that while 4K is on its way to becoming a standard resolution, the fact that said resolution has more pixels to process in each frame means that the number of cores needed in the GPU , also. as support units, increase in number and with it the area of the same.
We cannot forget that despite the enormous power over the role of GPUs such as NVIDIA’s RTX 3090, we find that the same manufacturer recommends the use of DLSS 2.0. The idea is none other than to render games at a lower resolution internally and then scale them up. In this way, the number of cores required is much less.
Consider the size of GPUs like the NVIDIA GA102 and TU102, which come close to what’s called the lithography limit, which is the maximum size per chip that a manufacturing node can support. This forced NVIDIA to go for solutions such as adding Tensor units for resolution scaling by deep learning as a temporary measure, when in general everything switches to using GPUs with multiple chips in order to continue scaling, especially now that the challenge for engineers is 4K with Ray Tracing.